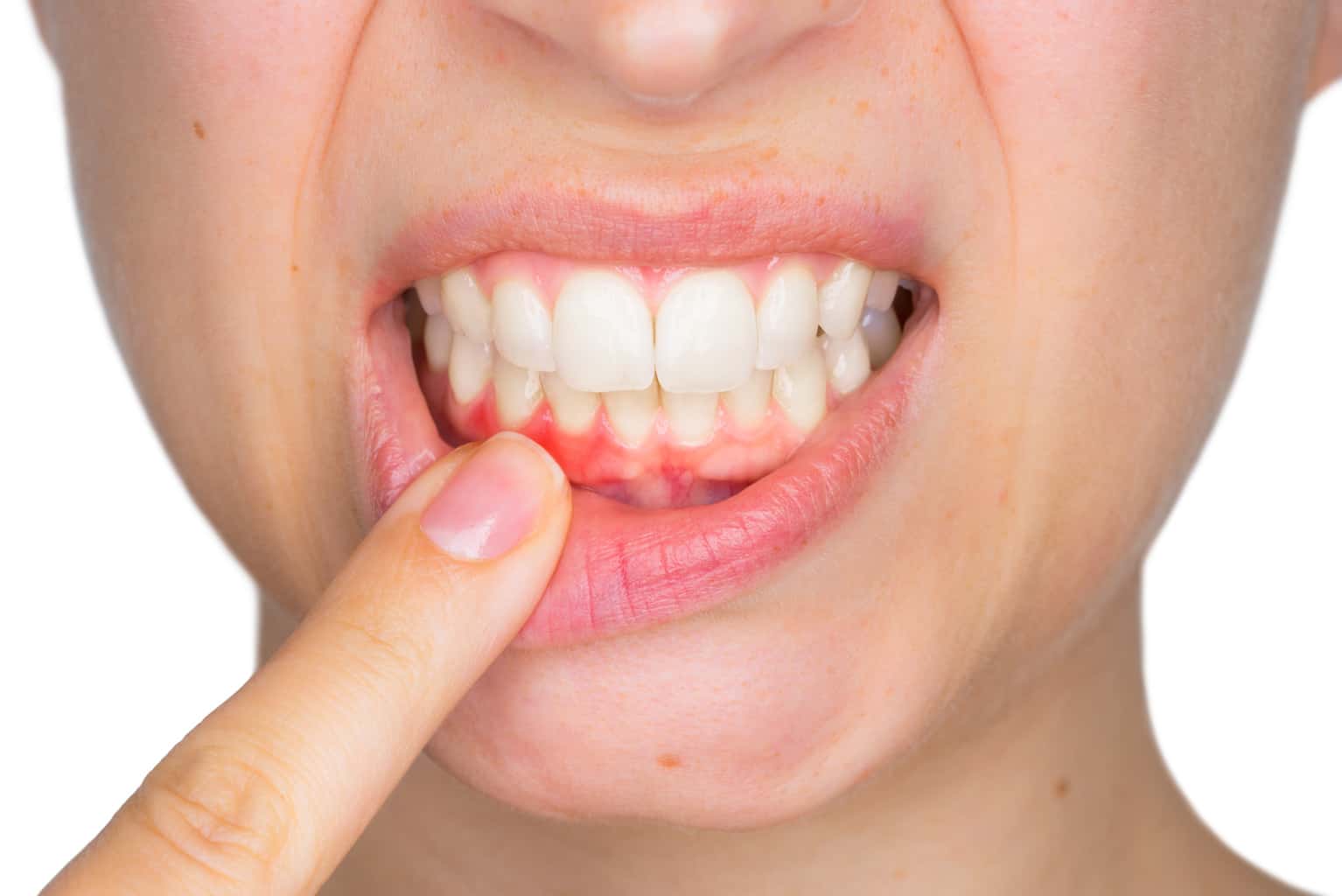
Introduction
Gum disease primarily occurs due to the buildup of plaque, a coating layer of bacteria, on the teeth and gums. If not removed properly, this plaque can harden into tartar, leading to inflammation and infection of the gum tissues. Over time, if left unattended, gum disease can progress, resulting in gum recession, tooth mobility, and even tooth loss.
The Role of Nutrition in Gum Disease Prevention
Nutrition plays an inevitable role in maintaining overall health, and its impact on oral health should not be underestimated. A balanced diet provides essential nutrients that support the immune system, help in tissue repair, and help prevent inflammation, all of which are crucial factors in preventing gum disease.
Vitamin C: The Gum Health Superhero
Vitamin C is one of the most well-known nutrients for its role in gum health. Without sufficient vitamin C, gums can become weak and susceptible to infection. Severe vitamin C deficiency can lead to bleeding gums and loose teeth, a condition called scurvy. To ensure gum health, include vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, and bell peppers in your diet.
Antioxidants and Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Inflammation is a hallmark of gum disease. Eating foods rich in antioxidants, like berries, leafy greens, and green tea, can help reduce the inflammation that contributes to gum problems. These antioxidants neutralize harmful free radicals that can damage gum tissues. Additionally, Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon and walnuts possess anti-inflammatory properties that can aid in reducing gum inflammation.
Calcium and Vitamin D for Strong Teeth and Gums
Calcium is important for the development and maintenance of strong teeth and gums. It works in combination with vitamin D, which helps the body absorb and utilize calcium effectively. Low levels of calcium can contribute to weakened gums and tooth decay. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt, as well as leafy greens, almonds, and fortified foods, are good sources of calcium. Vitamin D can be obtained from exposure to sunlight and dietary sources like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products.
Phosphorus for Oral Health
Phosphorus is another essential mineral for maintaining healthy teeth and gums. It plays a role in strengthening tooth enamel and supporting proper gum function. Dairy products, lean meats, poultry, fish, and nuts are excellent sources of phosphorus.
Water: Nature’s Cleanser
While water isn’t a nutrient, its role in maintaining oral health cannot be overlooked. Drinking water helps rinse away food particles and bacteria from the mouth, preventing the buildup of plaque and reducing the risk of diseases of the gum. Staying well-hydrated is crucial for overall oral hygiene.
The Role of Probiotics
Probiotics, often associated with gut health, can also benefit oral health by promoting a healthier balance of bacteria in the mouth. Yogurt with live cultures and certain probiotic supplements may be beneficial for the gum.
Practical Tips for Gum Disease Prevention Through Nutrition
- Ensure your diet includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods to support overall health, including the health of your gums.
- Sugars and refined carbohydrates promote the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth. Reduce its consumption.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help maintain oral hygiene.
- Include vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables, antioxidants, calcium, and phosphorus sources in your meals.
- Explore probiotic-rich foods and supplements to promote a healthier balance of oral bacteria.
- Even with a healthy diet, regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial for preventing and addressing gum disease.
Conclusion
Nutrition plays a vital role in preventing gum disease and maintaining overall oral health. A balanced diet rich in nutrients, like vitamin C, antioxidants, calcium, and phosphorus, can help strengthen gums, reduce inflammation, and support strong teeth. Additionally, staying hydrated and limiting sugary foods and beverages are essential components of a gum-friendly diet. By making mindful dietary choices and maintaining good oral hygiene practices, individuals can take proactive steps towards preventing gum disease and enjoying a healthy smile for years to come.