Introduction
Oral piercings have gained popularity as a form of self-expression and body art, allowing individuals to decorate their mouths with jewelry, studs, and rings in various locations, including the tongue, lip, and cheek. While oral piercings may be trendy, they come with potential health risks, including an increased susceptibility to gum disease. Let’s understand more about the connection between oral piercings and gum disease, discussing the potential consequences and offering advice on how to minimize the risks associated with these accessories.
Oral Piercings and Gum Disease
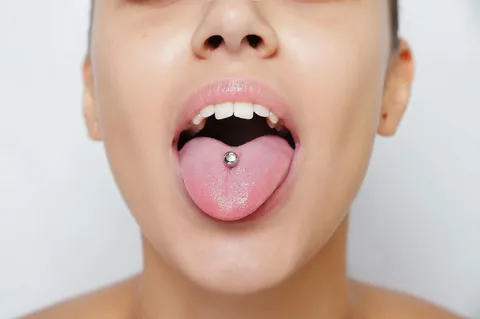
The relationship between oral piercings and gum disease is complex, but it largely depend on the following factors:
- Oral piercings, especially those located on the lips or cheeks, can rub against the gums, causing irritation and injury. This constant irritation can result in the inflammation of gums and increased susceptibility to gum disease.
- The mouth is home to a wide range of bacteria. Oral piercings create an entry point for oral bacteria to enter the bloodstream, increasing the risk of infection. Bacteria introduced through oral piercings can lead to gum infections, such as gingivitis and periodontitis.
- The presence of oral piercings can lead to dental issues.
Preventing Gum Disease associated with Oral Piercings
While the risks associated with oral piercings and gum disease are real, there are steps individuals can take to minimize these risks and continue to enjoy their piercings:
- Opt for a professional piercing studio with an excellent reputation. A skilled piercer will minimize the chances of complications during and after the piercing process.
- Select high-quality jewelry made from materials like surgical stainless steel, or titanium. Avoid nickel-containing jewelry, as it can lead to allergic reactions and complications.
- Maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial. Brush and floss your teeth regularly, and rinse your mouth with an alcohol-free, antimicrobial mouthwash to minimize bacteria growth.
- When speaking or eating, be careful of your oral jewelry to avoid accidental damage to your teeth and gums. Remove the jewelry if it interferes with daily activities.
- Avoid playing with or twisting your oral jewelry, as this can lead to gum irritation and dental damage.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups to monitor your oral health. Your dentist can identify any potential issues and provide guidance on maintaining a healthy mouth with oral piercings.
- If you notice any signs of infection, irritation, or gum issues around your oral piercing, seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can prevent more severe complications.
Conclusion
Oral piercings can be a trendy form of self-expression, but they come with associated health risks, including an increased susceptibility to gum disease. The constant irritation, potential bacterial entry, and dental damage can all contribute to this risk. However, with proper care, awareness, and professional guidance, people can enjoy their oral piercings while minimizing the chances of gum disease. Remember that the key to a safe and stylish experience with oral piercings is maintaining oral hygiene and addressing any issues that may arise. If you decide to get an oral piercing, do so with caution and educate yourself about the proper care to ensure a healthy, beautiful smile for years to come.
