Is Gum Disease Contagious?
The simple answer is no; gum disease itself is not directly contagious in the same way that the flu or a cold is. You won’t catch gum disease by sharing a meal with someone, kissing, or even through close contact. Gum diseases develop as a result of complex interactions between an individual’s oral hygiene, genetics, and lifestyle factors. However, there are important factors to consider:
- Bacterial Transfer: While gum disease itself is not contagious, the bacteria responsible for gum disease can be spread. For example, when an infected person shares eating utensils, kisses, or engages in activities that involve saliva exchange, the bacteria causing gum disease can be transferred. However, this transfer doesn’t guarantee that the recipient will develop gum disease, as other factors play a significant role.
- Genetic and Lifestyle Factors: An individual’s susceptibility to gum disease is influenced by genetics and lifestyle. Some people may have a genetic predisposition that makes them more prone to gum disease. Additionally, factors like smoking, poor oral hygiene, and a diet high in sugar can increase the risk of developing gum disease.
- Oral Hygiene and Periodontal Health: The most critical factor in developing gum disease is an individual’s oral hygiene. Regular and effective brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups play a significant role in preventing and managing gum diseases.
Preventing the Spread of Gum Disease Bacteria
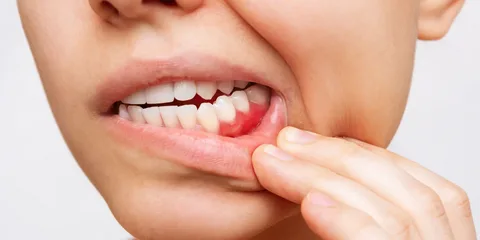
To minimize the risk of spreading gum disease bacteria, consider the following tips:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce the buildup of harmful bacteria in the mouth. Proper oral care is the first line of defense against gum disease.
- Avoid Sharing Oral Items: Do not share toothbrushes, dental appliances, or utensils with others, especially if you know they have gum disease. This can help reduce the chances of bacterial transfer.
- Seek Treatment Early: If you suspect you have gum disease, it’s essential to consult a dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening and reduce the risk of bacterial transmission.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Raise awareness about the importance of gum disease prevention and oral hygiene within your community and among your friends and family. Knowledge is key to better oral health.
Conclusion
Gum diseases, while not directly contagious, involve a complex interplay of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and oral hygiene. However, the bacteria responsible for gum diseases can be transferred through close contact and sharing items, though this does not guarantee the development of gum disease in the recipient. Preventing gum disease requires a combination of good oral hygiene practices, a healthy lifestyle, and early intervention when necessary.
The key step is maintaining excellent oral hygiene, avoiding the sharing of oral items, and seeking professional dental care protect yourself and your loved ones from the potential spread of gum disease bacteria. By staying informed and practicing good oral health habits, you can reduce the risk of gum diseases and maintain a healthy smile for years to come.
